After learning about the
basics of Java Programming, it's time to switch to the most important topics of Java. In this tutorial,
we are going to learn about the basic concept of oops in Java. OOPs
stand for Object Oriented Programming.
What is object-oriented programming in Java?
These days most prominently, 2 out of 4 types of
programming paradigms
are used. These are procedural programming and
object-oriented programming. Procedural programming considers
procedures or methods as the most essential components of a language.
Whereas Object-oriented programming focuses on real time entities called
objects. OOP is basically about creating objects that bind data and methods
together in an encapsulated unit known as class.
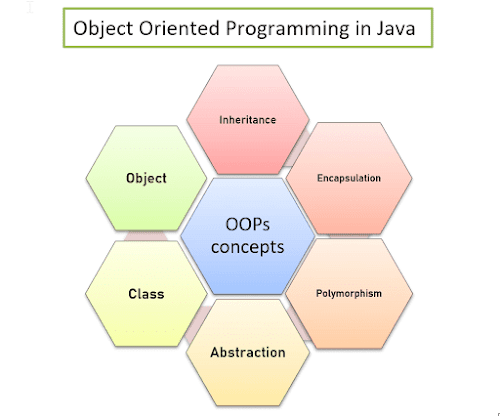
Object oriented programming paradigm provides several features like
encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance and
polymorphism. All these features together provide an essence of
reality to Java. Thus making it more secure, reliable, portable and
modularized.
Advantages of Object-Oriented Programming
- Breaks the whole program into smaller modules, which is helpful in identifying problems and making changes. Hence, OOPs increases modularity.
- Reduced complexity; as the use of real world models increase the clarity in the code.
- Code re-usability; through this model of real world entities, class and objects. The extent of code reusability increases very much. The class itself acts as a blueprint for creating more and more objects.
- It binds the data and code into a single unit.
- Abstraction provides more security of data; we can limit the scope of data in a method or class, so that anyone cannot modify the data, without consent.
- It is actually faster than other programming paradigms and easier to execute.
- It focusses on making the code 'DRY' - Don't Repeat Yourself by making it easier to modify, debug and maintain the code.
- Also the reuse of code/software reduces the overall cost of development
Most Essential terms in Object Oriented Programming
Class
A class is a inbuilt/user-defined blueprint, which is used while
creating objects. Or it can be called as a collection of objects. It
represents the properties and behaviour of a particular set of
objects.
Declaring a class in java:
class className{
/* statements */
}
* We can
also add modifiers like public, private, protected before the class
keyword.
public class TestClass{
/* statements */
}
* The className can be any
valid identifier
created keeping in mind the same conventions for declaring
variables.
* Going with conventions, Class name identifier should always have
first letter capital.
* Class actually doesn't consume any space in memory, until unless
its object is created.
* In every program, there needs to be one public class. And in
that public class, we have to make the main method.
* Classes can be of different types: Nested Classes, Anonymous Classes
etc.(Going to discuss in next tutorials)
Object
It is the most essentially fundamental concept of OOPs. An object is
created from a Class. It can be physical or logical. It is actually an
instance of the class which has a behaviour(methods), state(attribute)
and name(object-name). It gets memory at run-time.
- The state of the object represents the properties it has, like for a class Car, its attributes or state can be carColor, carType etc.
- The behaviour can be referred to the things the object can do, like for class Car, behaviours are driving, playing music etc.
- Name is the unique name given to that object. This is the main clause which enables interaction between different objects.
public class Dog{
/* states or attributes */
String breed;
int age;
String color;
/* Behaviour or methods */
void bark(){
//statements...
}
void eat(){
//statements...
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d1 = new Dog();
/* d1 is an object of class Dog */
}
}
* In this example, d1 is the object of class Dog, or we say
d1 is an instance of class Dog.
* This instance d1, will have its own set of properties from class Dog,
like it will have a particular breed, age, color etc. With its
particular set of behaviours like its specific way of barking, eating
etc.
Polymorphism
The term polymorphism is made up of 2 terms: poly and morph, meaning
many and forms, simultaneously. It is the concept in which a single
method can be expressed in different forms by changing its signature.
This would be clear to you through the following example:
class Sample{
public void sum(int a, int b){
System.out.println(a+b);
}
public int sum(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
public float sum(float a, float b, float c){
return a+b+c;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Sample.sum(1,2);
int sum1 = Sample.sum(12,13);
System.out.println(i);
float f = Sample.sum(12.3,1.1,0.1);
System.out.println(f);
}
}
OUTPUT
3
25
13.5
* In this example,
polymorphism is implemented by changing the number arguments or
changing the return type of the method, by keeping the name same.
* Polymorphism is usually achieved by 2 ways:
method overriding and method overloading. Also making an
operator exhibit different behaviours at different instances is known
as operator overloading. For example:
use of '+' operator. In case of Strings, it is concatenation
and in case of integers it is addition.
Inheritance
It is also an essential concept of Object Oriented programming in
Java, which enables one class to inherit the properties of any other
class, specifically known as parent class using the
extends keyword. This parent-child relationship is very much useful in case of
creating new classes which either has same properties as of another
class or has some modifications in those properties.
The class which inherits the properties of the parent class is known
as Sub-class or child class, whereas the class from where it inherits
those properties is called Super-class or parent class.
Infact the objects also inherit properties from the parent objects. It
is used to achieve runtime polymorphism.
class Animal{
//statements..
}
class Mammal extends Animal{
//statements..
}
* The class Mammal inherits the properties of Animal class, it
can either use the same methods of Animal class or can modify them
according to its need.
* Inheritance is of many types like: single level, multiple,
multilevel, hierarchical etc.
* Java
do not supports supports multiple inheritance.
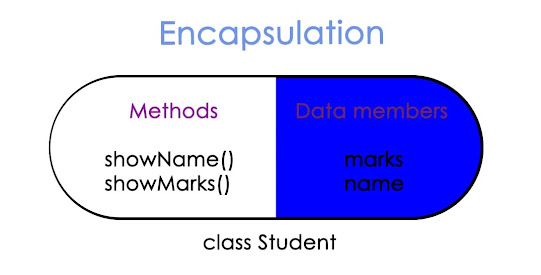
Encapsulation
Encapsulation can be defined as wrapping up or binding of data and
methods/code into a single unit. The most effective example of
encapsulation is the java class itself. As it contains or binds both
the data and code together in it.
class Car{
/* data */
private String type;
private int model;
/* code or methods */
public void playMusic(){
//statements..
}
public void start(){
//statements..
}
}
* It enables the feature of Data-hiding using the
private access modifier alongwith, by making the data
un-available to the outside world. And can only be accessed by the
class methods itself.
Abstraction
It is the mechanism of hiding the inner details of a functionality and
showing only the outer details or the essential information to the
user. For example, in case of ATM, we only see that we insert the
card, enter the pin and amount, and we get money, despite getting
notified what else is going inside the ATM machine.
Abstraction can be achieved by abstract class or methods or by using
interfaces.
public abstract class Test{
public abstract void doWork();
}
* We would be learning about these topics in the future tutorials.
Disadvantages of Object Oriented Programming
- It has a steep learning curve: it often takes time for learning about the thinking process in OOPs.
- Due to modularity, the program divides into smaller segments, thus increasing the overall length of program.
- Object Oriented programs are typically slower than procedural program, as they require more instructions to be executed.
- A verbose syntax